单选题
编号:2693912
1. A variable is normally distributed with a mean of 5.00 and a variance of 4.00. Calculate the probability of observing a value of negative 0.40 or less. That is, calculate P (Xi ≤ -0.40) given X is distributed as N(5,4). Use this excerpt from the cumulative distribution function for the standard normal random variable table to calculate your answer.
Cumulative Probabilities for a Standard Normal Distribution
P(Z ≤x) = N(x) for x ≥ 0 or P(Z ≤ z) = N(z) for z ≥ 0
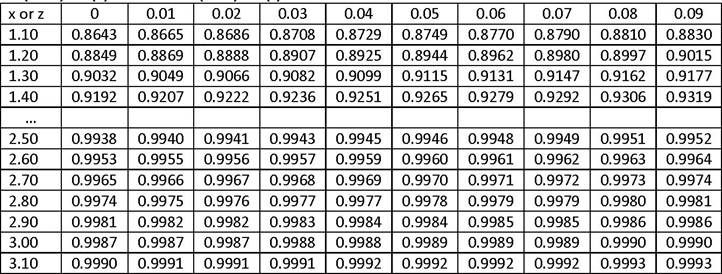
The calculated value is closest to:
Cumulative Probabilities for a Standard Normal Distribution
P(Z ≤x) = N(x) for x ≥ 0 or P(Z ≤ z) = N(z) for z ≥ 0

The calculated value is closest to: